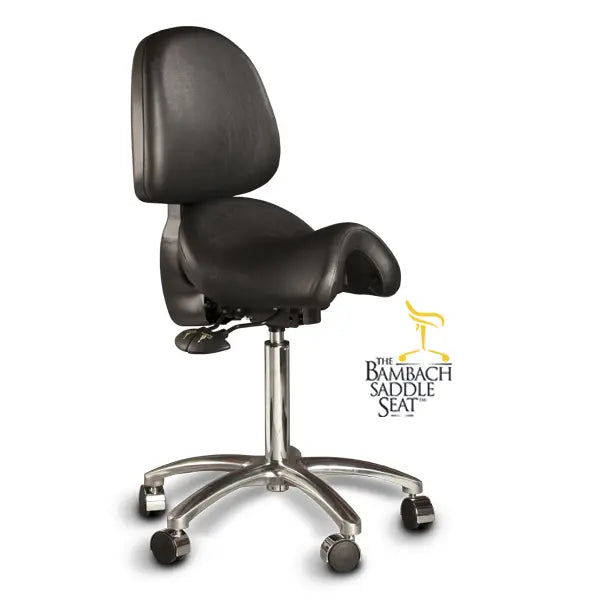
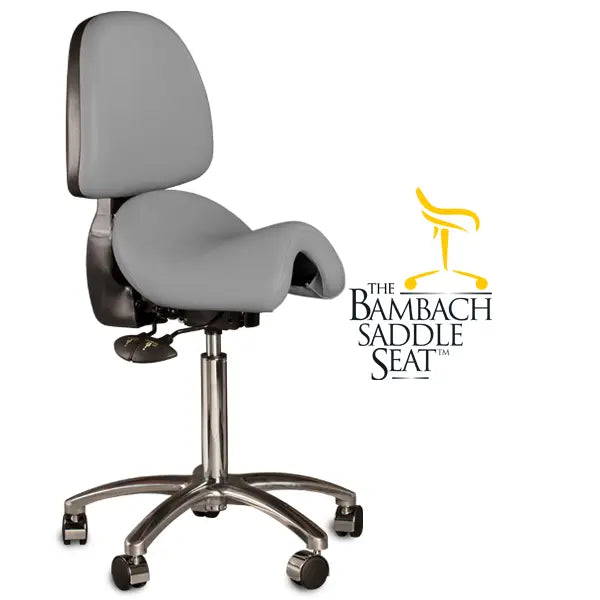
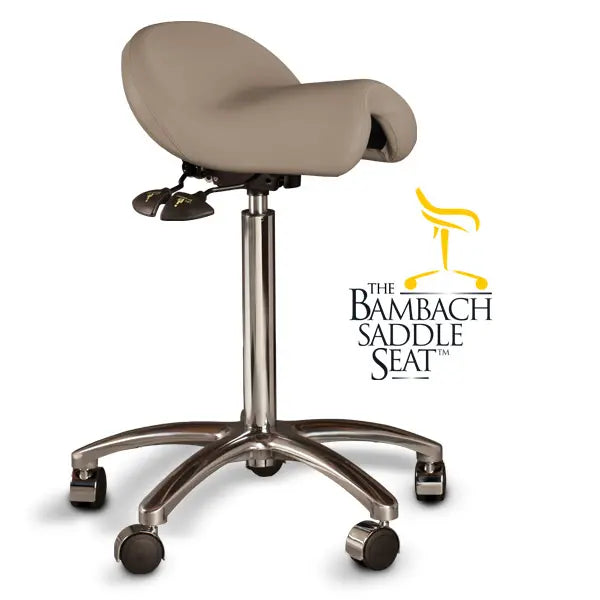
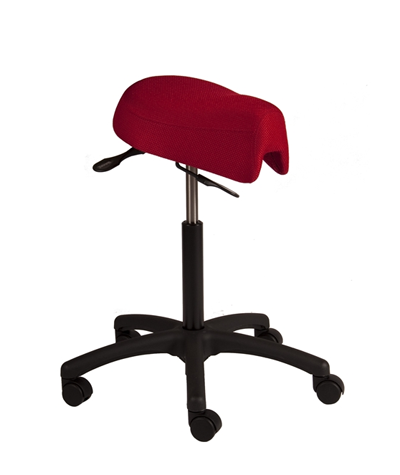
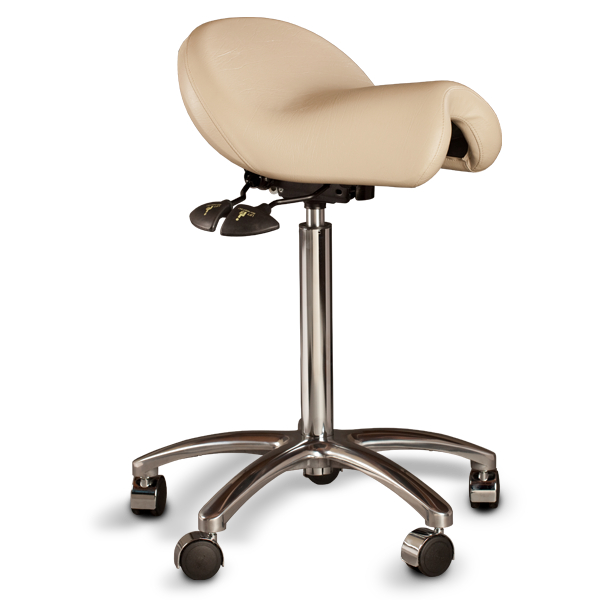
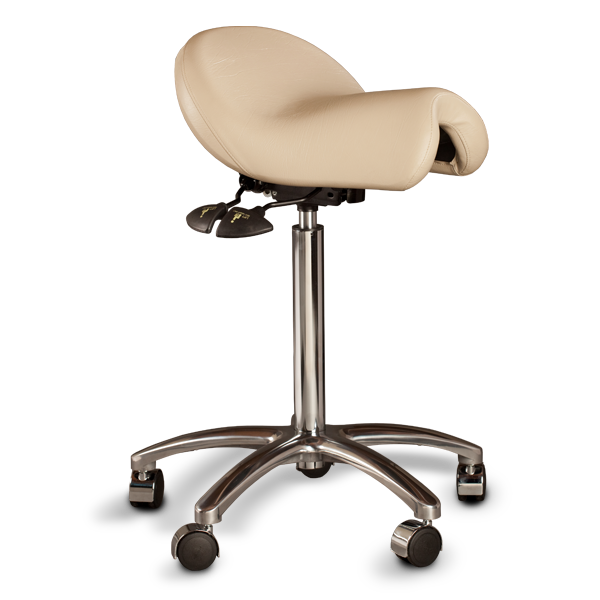
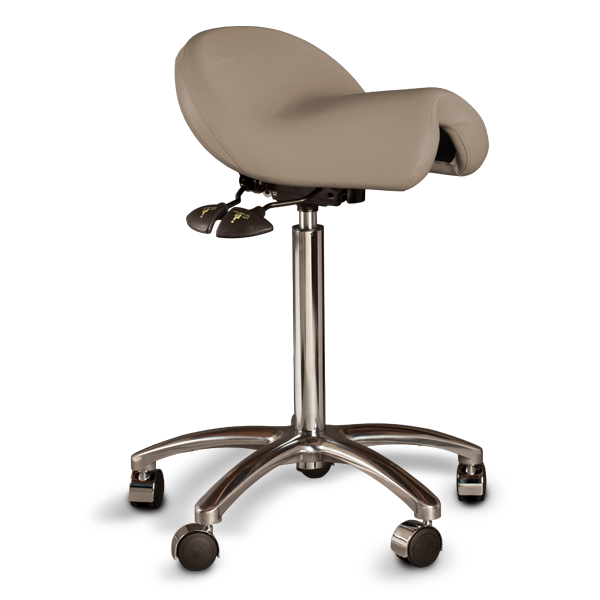
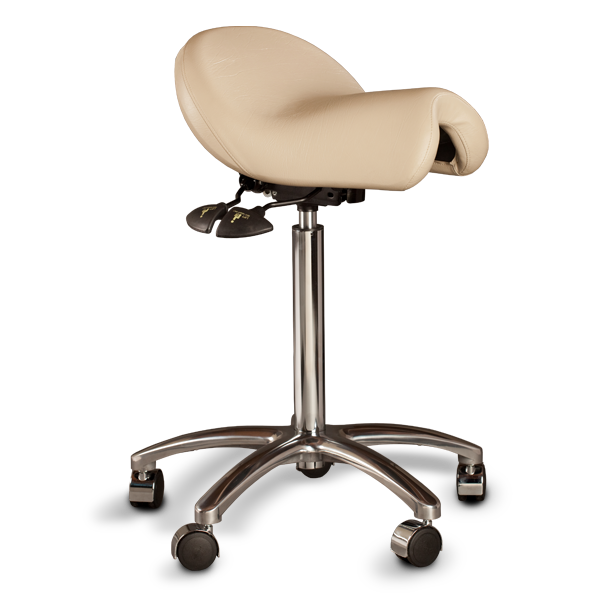
Ergonomic Saddle Chairs*
- The strongly declining position of the upper legs rotates the pelvis forward and curves the lower back into an anatomically correct position of lordosis.
- The riding-style sitting posture makes it easy to preserve a natural, upright posture, just as if you were standing, but without the fatigue and stress on your legs.
- Saddle seats puts no pressure on your knees, leaves your feet free to operate equipment or move around your work area, as well as supporting and stabilizing your body with its high, saddle posture.
- Saddle chairs can help alleviate hip pain by reducing pressure on the hips and lower back.
- A significant benefit of saddle stools compared to traditional seating is their ability to promote proper posture. A saddle stool's unique design encourages a more natural sitting position, with an open hip angle and a forward tilt.
- Sitting in a saddle opens up the angle between your hips and knees to 135° (compared to 90° for an office chair). As a result, your spine is held in its natural curve, which prevents you from slouching and thereby reduces tension and pain in the neck, shoulders and lumbar region.
- The Bambach Saddle Seat provides relief for sciatica suffers: By positioning the thighs in their resting position at 45°, the sciatic nerve is in its neutral position and provided the pelvis is upright which it is on a Bambach, pressure on the sciatic nerves is reduced.
- There are five factors every practitioner should consider when picking out their saddle. These factors are 1) pelvic width, 2) torso size, 3) leg length, 4) height, and 5) hip flexibility.
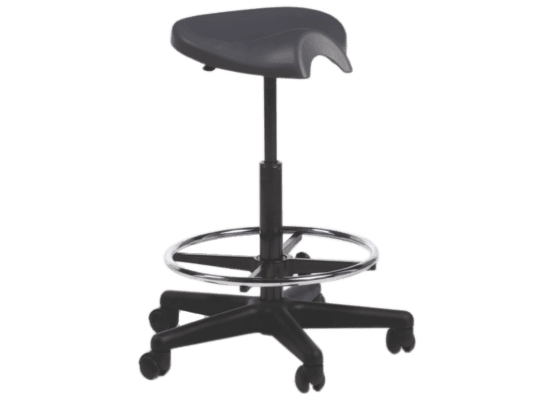
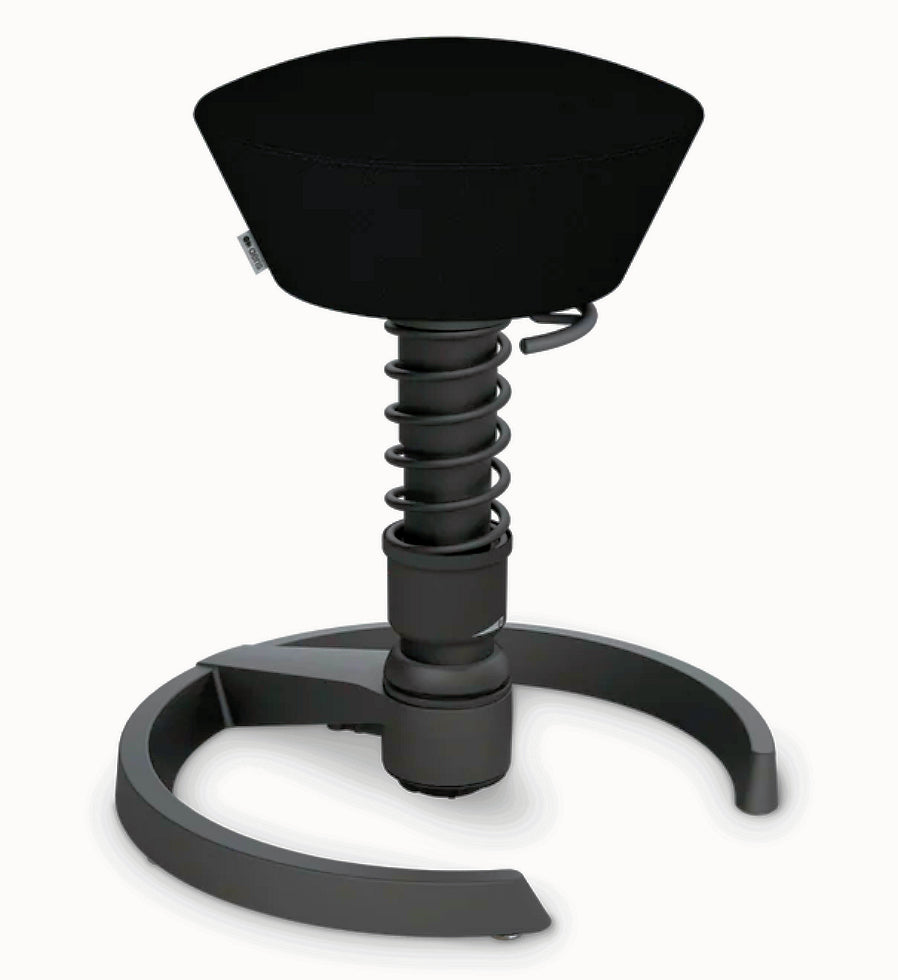
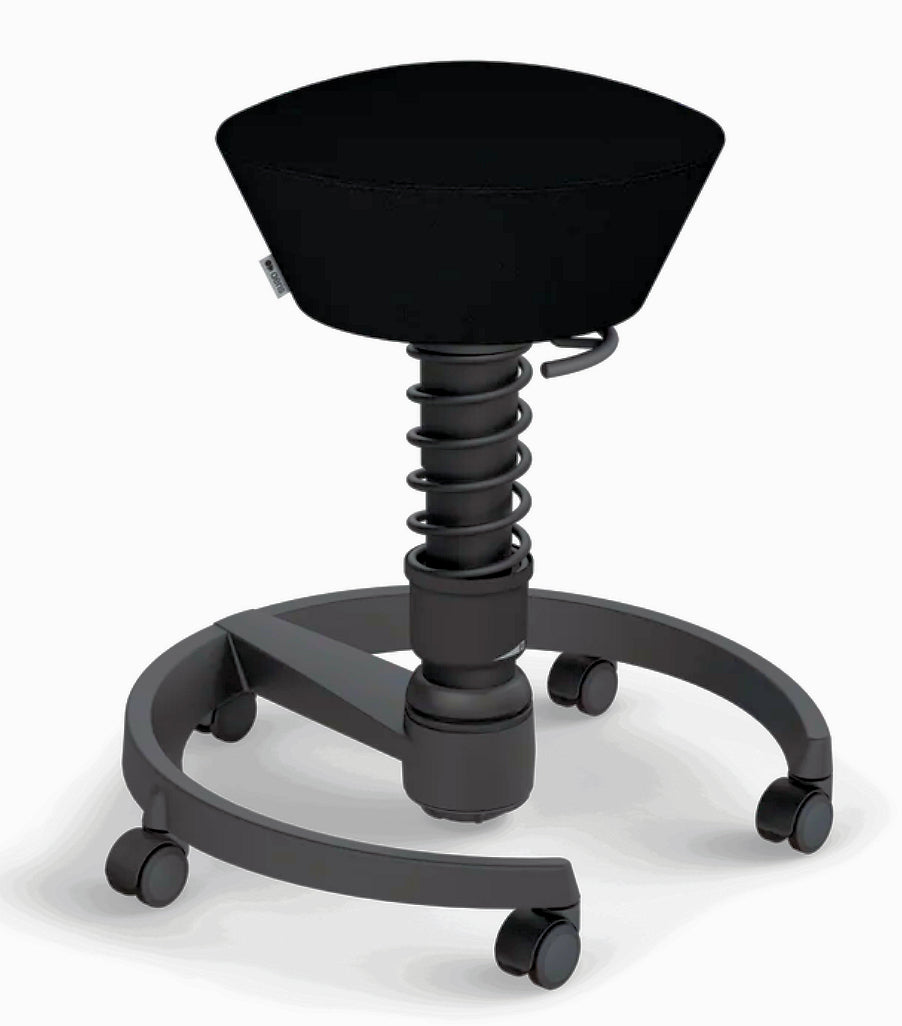
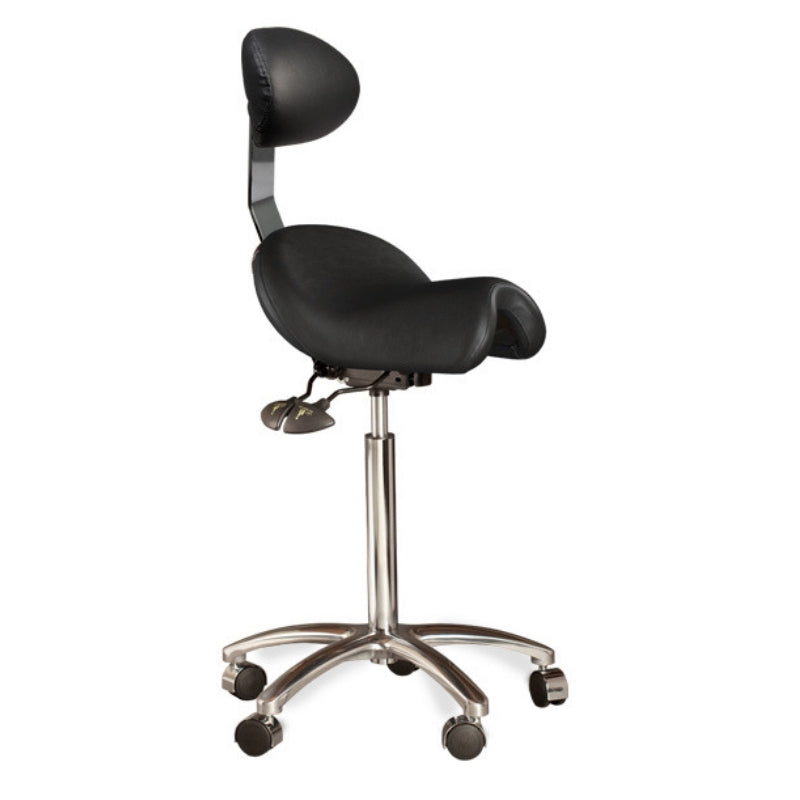
A saddle chair uses the same principles in its design as an equestrian saddle. It is equipped with a chair base on casters and a gas cylinder for adjusting the correct sitting height. The casters enable moving around and reaching out for objects while sitting. Some saddle chairs have backrests, but most do not. Some models also have a swing mechanism in the seat, which increases small movement mobility to the low back and stomach for the goal of better circulation in soft tissues.
Riding-like sitting on a saddle chair differs from sitting on a conventional chair. Saddle chair users sit 20–30 cm higher, which puts the hips and the knees into a 135° angle, compared to the 90° angle typically associated with sitting on a traditional chair.
Because the saddle chair is higher than a normal office chair, the desk has to be higher as well. For this purpose there are desks that can be electronically or mechanically adjusted to fit the user. A saddle chair can also be used with a normal office desk, but then the desk has to be lifted up with height extension pieces or most practically with electric or gas spring mechanisms.
The saddle chair seat is either solid or divided. A divided seat reduces pressure on the perineum, but also on the coccyx and the genitals on the pubic bone, and lowers the temperature in the genital area. A divided seat is thought to be healthier than a solid seat, for women but even more so for men, whose genitals are all outside the body and easily pressed by the furniture.
Saddle chairs usually have height adjustments but also a tilt mechanism. There are divided saddle chair models with adjustable gap between the two seat parts and also swing mechanism, which increases the small movements of the pelvic and stomach. The goal of this is to increase circulation in the soft tissues for better tissue metabolism. Accessories, such as elbow and wrist supports, are available for saddle chairs to make different work tasks easier.
* Authorized Canadian Bambach Distributor